“Replaceable You”: A GizmoMD Book Interview with Author Mary Roach
“We can rebuild him. We have the technology. We can make him better than he was. Better . . . stronger . . . faster.” These iconic words were part of the opening lines of the hit TV series, The Six-Million Dollar Man,…
The Latest
Rapid Saliva Test Could Improve Concussion Detection
A new saliva based diagnostic tool developed at the University of Waterloo is being positioned as a faster and more objective way to identify concussions in real time. The technology was created by HeadFirst, a startup co-founded by a Waterloo alumnus who drew on his own experiences with sports related head injuries to address the long standing challenge of subjective concussion assessments. Traditional sideline evaluations depend heavily on self reported symptoms and observational checklists, which can be unreliable when athletes minimize or fail to recognize signs of injury. The new device instead measures a specific biomarker released by the brain…
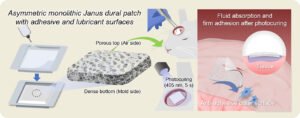
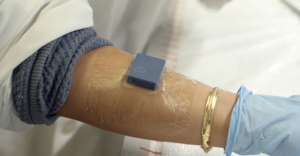
Light Activated Dural Patch Speeds Watertight Neurosurgical Sealing
Researchers at Pusan National University have developed a light activated tissue adhesive patch designed to rapidly and securely seal tears in the dura mater, the protective membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Dural tears, whether accidental or intentional during neurosurgery, can lead to cerebrospinal fluid leakage that increases the risk of headaches, delayed healing, and serious infections. Existing sealants and suturing techniques often struggle to provide a reliable watertight closure and can swell excessively, compressing nearby brain tissue or causing unwanted adhesions. The new patch aims to solve these problems by combining strong, controllable adhesion with minimal swelling and…
Sweat Based Hormone Sensor Could Transform Sleep And Circadian Health
Scientists at the University of Texas at Dallas, in collaboration with Texas based company EnLiSense, have developed a wearable sensor that measures two key hormones in sweat to better understand the body’s sleep wake cycle. The device continuously tracks cortisol, which is associated with alertness and stress, and melatonin, which signals the body to prepare for sleep. Unlike most consumer sleep trackers that rely on motion or heart rate as indirect indicators, this sensor directly measures biochemical signals, offering a more precise window into circadian rhythms and sleep quality. The sensor uses an electrochemical system to detect very low concentrations…
Bioengineered Skin Grafts Offer New Hope For Burn Victims
Researchers at the University of Zurich have developed advanced bioengineered skin grafts that could significantly improve treatment for people with severe burns. Building on more than fifteen years of work, the team has created living skin grown from a patient’s own cells, an approach that aims to overcome the limitations of traditional grafts, which often lack elasticity, do not grow with the patient, and can lead to functional and cosmetic problems over time. The research also led to the founding of the spin off company Cutiss in 2017, which is working to translate this technology into clinical practice. The article…
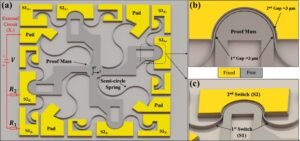
Tiny Sensor Could Be a Game Changer For Head Injuries
A research team at King Abdullah University of Science & Technology (KAUST) has developed a fingernail‑sized sensor that can instantly detect hazardous head impacts, offering a potential breakthrough for safety in sports, transportation, and other high‑risk environments. The project carries a personal motivation: one of the researchers lost his brother to an undetected head injury, which inspired the development of a device that can distinguish minor bumps from dangerous blows the moment they occur. The sensor acts like a mechanical safety switch that responds to sudden acceleration. When a strong impact occurs, the internal structures make physical contact, closing an…
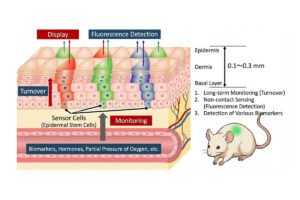
Living Sensor Display Turns Engineered Skin Into a Biological Monitor
Researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo have developed an engineered skin graft that functions as a living sensor display. The graft fluoresces in response to internal biomarkers such as inflammation, allowing long‑term monitoring of biological states without the need for blood sampling. The team created the sensor by engineering epidermal stem cells so that they activate a fluorescent signal when specific molecular pathways associated with inflammation are triggered. When transplanted onto immunodeficient mice, the graft remained stable over long periods and reliably increased or decreased fluorescence in response to inflammatory stimuli. This demonstrated that…
Comfortable New Wearable Lets Pregnant Women Measure Fetal Heart Rate at Home
Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology have developed a new wearable garment that allows pregnant women to measure the heart rate of their unborn baby at home in a more comfortable and practical way. The project was led by PhD researcher Yijing Zhang from the Department of Electrical Engineering, who focused on solving a persistent problem in fetal monitoring. Many existing home fetal heart rate devices rely on gel‑based electrodes that must be placed directly on the skin. These gels can feel cold or sticky, may irritate the skin, and often make the monitoring process inconvenient for everyday use. As…
Skin‑Attachable Ultrasonic Sensor Enables Cuffless Blood Pressure Tracking
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology have developed what they describe as the first skin‑attachable ultrasonic sensor capable of measuring blood pressure without the need for a traditional cuff. The work focuses on creating a more comfortable and continuous method for monitoring blood pressure, which is one of the most widely used indicators of cardiovascular health. Conventional cuff‑based devices can be inconvenient, bulky, and unsuitable for continuous use, especially outside clinical settings. The new sensor aims to address these limitations by offering a lightweight, wearable alternative that can be…
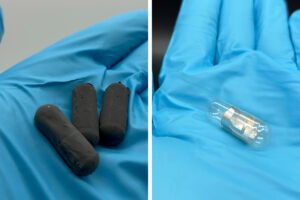
Biodegradable Smart Pills Signal When Medication Is Taken
MIT engineers have developed a new type of ingestible capsule that can send a signal from inside the stomach to confirm that a medication has been swallowed. The technology is designed to address a long‑standing challenge in medicine: ensuring that patients take their medications consistently and on schedule. Poor adherence is a major barrier to effective treatment for many conditions, including chronic infections and diseases that require strict dosing routines. The MIT team created a system that works within the familiar format of a standard pill capsule while adding a simple way to verify ingestion in real time. The capsule…
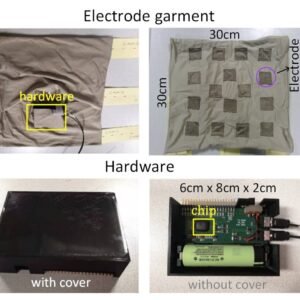
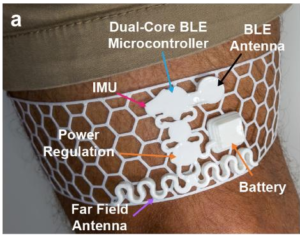
AI Wearable Detects Early Frailty Signs to Support Safer Aging
Researchers at the University of Arizona have developed a soft, comfortable wearable device that uses artificial intelligence to detect early signs of frailty, a condition that significantly increases the risk of falls, hospitalization, and loss of independence among older adults and people with disabilities. Frailty is common but often underdiagnosed because it is usually assessed only after a major adverse event has already occurred. The team’s goal is to shift care from reactive to preventative by enabling continuous monitoring in everyday life. The device takes the form of a soft mesh sleeve worn around the lower thigh. It continuously monitors…