“Replaceable You”: A GizmoMD Book Interview with Author Mary Roach
“We can rebuild him. We have the technology. We can make him better than he was. Better . . . stronger . . . faster.” These iconic words were part of the opening lines of the hit TV series, The Six-Million Dollar Man,…
The Latest
Ultralight 3D Aerohydrogel Scaffold Allows Human Brain Cells to Grow and Communicate More Naturally
A recent breakthrough from researchers at Kiel University in Germany introduces an ultralight 3D aerohydrogel material that allows human brain cells to grow, connect, and exchange signals in ways that closely resemble real neural tissue. The team set out to solve a long‑standing limitation in neuroscience research. Conventional 3D cell culture systems are often too rigid or too unstable to support the delicate, dynamic interactions that define neuronal communication. As a result, many laboratory models fail to capture how brain cells behave in living tissue. The Kiel group developed a new scaffold that overcomes these constraints by combining structural stability…
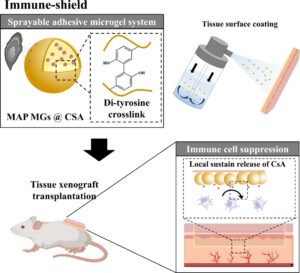
Spray‑On Immune Shield Coating Protects Transplanted Organs Without Systemic Immunosuppression
A recent advance from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and Ewha Womans University in Korea introduces a spray‑on coating that adheres directly to transplanted organs and delivers immunosuppressive drugs locally, offering a potential way to reduce or even eliminate the need for lifelong systemic immunosuppressants. Organ transplantation remains the most effective treatment for organ failure, yet patients must take continuous immunosuppressive medication to prevent rejection. These drugs circulate throughout the body and can cause serious side effects, including kidney toxicity and heightened infection risk. The research team set out to solve this long‑standing problem by shifting immunosuppression from…
3D‑Printed Beating Heart Model Gives Surgeons a Realistic Way to Practice Complex Procedures
Researchers at Washington State University have created a 3D‑printed heart model that can beat, pump fluid, and mimic the mechanical behavior of real cardiac tissue, offering surgeons a more realistic way to practice complex procedures before entering the operating room. The project grew out of a need for training tools that better replicate the feel and movement of a living heart. Traditional silicone models are static and lack the dynamic qualities that make cardiac surgery so challenging. The WSU team set out to build a model that could reproduce the motion, pressure changes, and tactile feedback of a functioning human…
3D‑Printed Biodegradable Bandage Delivers Natural Antimicrobials to Help Chronic Wounds Heal
A new effort from the University of Mississippi is advancing how clinicians might treat chronic wounds by developing a 3D‑printed bandage that delivers natural antimicrobial compounds while supporting tissue repair. Chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers and pressure sores can persist for months or years, often because poor circulation limits oxygen supply and slows the body’s ability to regenerate skin. These wounds are also highly vulnerable to infection, and long‑term antibiotic use can contribute to resistance. The Ole Miss team set out to design a customizable scaffold that could protect the wound, promote healing, and reduce infection risk without relying…
Microneedle Skin Patch Provides a New, Painless Way to Monitor Immune Health in Real Time
A new advance from The Jackson Laboratory introduces a painless microneedle skin patch that can monitor immune activity directly from the skin, offering an alternative to blood draws and surgical biopsies. Researchers at JAX, working with MIT, designed the bandage‑like device to capture inflammatory signals within minutes and collect specialized immune cells within hours, giving clinicians access to information that is often difficult or impossible to obtain through routine testing. The patch is about the size of a quarter and uses tiny microneedles to sample immune cells that reside in the skin, a population that plays a central role in…
Human Mini‑Bladder Model Reveals Why Some Urinary Tract Infections Keep Coming Back
A research team at Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland has developed a human mini‑bladder model that uncovers a key mechanism behind recurrent urinary tract infections, offering new insight into why some infections return even after treatment. The scientists created a three dimensional organoid that mimics the structure and function of the human bladder, including the layered architecture of the urothelium. This model allowed them to observe how uropathogenic bacteria interact with bladder tissue in ways that are difficult to study in animals or traditional cell cultures. The researchers found that certain bacteria can invade deeper layers of…
Lightweight Robotic Exoskeleton Helps Stroke Survivors Regain a More Natural Walking Pattern
Engineers at the University of Utah have introduced a lightweight robotic exoskeleton designed to help stroke survivors walk with greater stability and symmetry, addressing one of the most persistent challenges in post‑stroke rehabilitation. Many individuals who experience a stroke develop long‑term gait impairments that make walking tiring, inefficient, and unsafe. Traditional therapy can improve mobility, but progress often plateaus, and existing robotic devices tend to be bulky, expensive, or limited to clinical settings. The Utah team set out to create a wearable system that is comfortable enough for daily use while still providing meaningful biomechanical assistance. The device attaches to…
Portable Ultrasound Sensor Brings Earlier Breast Cancer Detection Into Homes and Clinics
A new development from MIT introduces a portable ultrasound sensor designed to make breast cancer screening more frequent, accessible, and timely for people at elevated risk. The research team created a compact imaging system that can be used at home or in a doctor’s office, addressing a long‑standing challenge in early detection. Many high‑risk individuals struggle to access regular imaging due to cost, scheduling barriers, or limited availability of specialized equipment. The MIT system aims to close that gap by offering a low cost, easy to use alternative that still provides clinically meaningful imaging. The device consists of a small…
Smart Catheter Sensor Uses Smartphone Readout to Detect UTIs Earlier and More Accurately
A recent project from Texas A&M University introduces a catheter‑mounted sensor that can detect urinary tract infections at an earlier stage by pairing real time bacterial monitoring with a smartphone app. Urinary tract infections remain one of the most common bacterial infections worldwide, and catheter associated UTIs account for more than half of all hospital acquired cases. Traditional diagnostic methods often require lab cultures that take days to return results, leaving clinicians with limited information during the critical early window when treatment is most effective. The Texas A&M team set out to create a faster, more accessible way to identify…
Electronic Mesh Implants Help Lab‑Grown Pancreatic Cells Mature Into Insulin‑Producing Tissue
A new study from the University of Pennsylvania reveals that an ultrathin electronic implant can guide lab‑grown pancreatic cells to mature into fully functional insulin‑secreting tissue, offering a potential path toward next generation cell therapies for diabetes. The research aimed to solve a long‑standing problem in regenerative medicine; although scientists can grow pancreatic islet cells from stem cells, these cells often remain immature and fail to release insulin reliably, limiting their therapeutic potential. The team developed a stretchable, hair‑thin mesh of conductive wires that integrates directly into three dimensional pancreatic organoids as they form. This mesh allows researchers to record…