“Replaceable You”: A GizmoMD Book Interview with Author Mary Roach
“We can rebuild him. We have the technology. We can make him better than he was. Better . . . stronger . . . faster.” These iconic words were part of the opening lines of the hit TV series, The Six-Million Dollar Man,…
The Latest
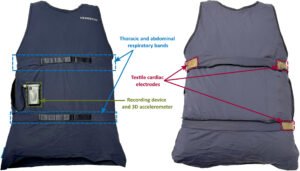
Smart Shirt Uses AI to Detect Epileptic Seizures in Real Time
A research team at Université de Montréal has developed a wearable smart shirt that can detect epileptic seizures in real time using artificial intelligence and integrated biometric sensors. Designed for comfort, discretion, and continuous monitoring, the shirt offers a promising alternative to traditional seizure detection systems, which often rely on bulky equipment or invasive procedures. The project’s goal was to create a textile-based solution that could monitor physiological signals associated with seizures and alert caregivers or medical personnel when an episode occurs. The result is a sensor-embedded shirt that tracks respiration, movement, and heart rate, all while maintaining the look…
Ultrasound Device Measures Blood Viscosity in Real-time Without Drawing Blood
A team of researchers at the University of Missouri has developed a non-invasive ultrasound device that can measure blood viscosity in real time, offering a new way to monitor cardiovascular health and disease progression. Blood viscosity—the thickness or stickiness of blood—has long been overlooked in routine diagnostics, despite its connection to heart disease, stroke, cancer, and other leading causes of death. The new device uses continuous-wave ultrasound to assess both viscosity and density simultaneously. It sends a steady sound wave through the bloodstream and analyzes how the wave interacts with the blood. A proprietary algorithm interprets these interactions to calculate…
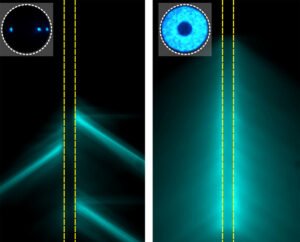
PRIME Fiber-Optic Device Enables Scalable Deep-Brain Stimulation With Unprecedented Precision
A new fiber-optic technology developed at Washington University in St. Louis is poised to transform neuroscience by enabling multi-site, reconfigurable optical stimulation deep within the brain. The device, called PRIME (Panoramically Reconfigurable IlluMinativE) fiber, delivers light to thousands of neural targets through a single, hair-thin implant—offering a minimally invasive solution to a long-standing challenge in optogenetics. Optogenetics uses light-sensitive ion channels to control neurons, allowing researchers to activate or silence specific cells. Traditional optical fibers, however, are limited to single-point delivery, making it impractical to study complex brain circuits that span multiple regions. To overcome this, the PRIME fiber integrates…
Heart Patch Uses Timed Drug Delivery to Heal Damage After Heart Attack
A new implantable patch developed by MIT engineers could dramatically improve recovery after heart attacks by delivering a sequence of therapeutic drugs directly to damaged heart tissue. Designed for use during open-heart procedures such as bypass surgery, the patch mimics the body’s natural healing timeline by releasing three different drugs over a two-week period. In preclinical studies, this approach reduced tissue damage by 50 percent and significantly improved cardiac function. The patch is built from a soft hydrogel embedded with rows of biodegradable microparticles. Each particle contains a specific drug and is engineered to degrade at a precise time point—early,…
Lung Cancer Breath Test Uses AI to Detect Volatile Biomarkers
A portable breath-based cancer screening tool developed at the University of Texas at Dallas is showing strong potential for early detection of thoracic cancers. By analyzing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath and applying machine learning, the device can identify cancer-linked chemical signatures with 90 percent accuracy in initial clinical tests. This approach could make noninvasive cancer screening more accessible, especially in primary care settings. The sensor is designed to detect eight specific VOCs that are known to correlate with cancer metabolism. These compounds are present in trace amounts and require highly sensitive detection methods. The biosensor uses screen-printed…
Researchers Develop Molecular Tools for Early Cancer Detection and Targeted Treatment
A new review from Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) explores how advanced biomedical tools are helping scientists study cancer in its earliest stages. The paper focuses on three key technologies—organoids, organs-on-a-chip, and 3D bioprinting—that replicate human tissue environments more accurately than traditional models. These platforms allow researchers to observe how cancer begins, progresses, and responds to treatment in ways that were previously impossible. Organoids are miniature, lab-grown versions of human organs created from stem cells. They mimic the structure and function of real tissues, making them ideal for studying tumor development and drug response. OHSU researchers use organoids to…
Wearable Brain Imaging System Reveals New Insights Into Multiple Sclerosis Progression
A team at the University of Nottingham has developed a wearable brain imaging system that enables researchers to study multiple sclerosis in real-world conditions. The device uses optically pumped magnetometers (OPMs) to measure magnetic fields generated by neural activity, offering a portable alternative to traditional magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems. This breakthrough allows patients to move freely during scans, capturing brain function in more natural states. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease that disrupts communication between the brain and body. Conventional imaging techniques often require patients to remain still in shielded rooms, limiting the ability to observe dynamic brain responses. The…
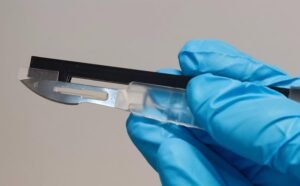
“Lab-on-a-Scalpel” Concept Integrates Electrochemical Sensor for Real-Time Tissue Diagnostics During Surgery
A new proof-of-concept surgical tool developed at UCT Prague could one day allow surgeons to analyze tissue biochemistry in real time. Researchers from the Sofer Group have created a prototype scalpel with an integrated electrochemical sensor, fabricated using 3D printing and carbon nanomaterials. This innovation, described as a “lab-on-a-scalpel,” represents a step toward smarter surgical instruments capable of detecting tissue conditions during procedures. The sensor is embedded in the scalpel handle and designed to detect low concentrations of metabolites under controlled laboratory conditions. It was produced using commercially available 3D printers and a composite material that combines plastic with conductive…
AI-Powered App Enables At-Home Sleep Stage Monitoring for Alzheimer’s Research
Sleep research is entering a new era of accessibility thanks to a wearable app developed by engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. The app, called BIDSleep, transforms consumer-grade Apple Watches into advanced sleep monitoring tools, allowing researchers to track sleep stages outside of clinical labs. This innovation could accelerate studies on sleep health and its connection to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Traditional sleep studies rely on polysomnography, a complex and expensive process that requires overnight monitoring in specialized facilities. These setups involve multiple sensors to measure brain activity, breathing, and movement, making them difficult to scale for large…
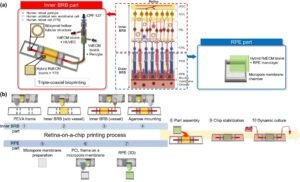
Retina-on-a-Chip Model Recreates Retinal Vein Occlusion for Drug Testing and Personalized Therapies
A new retina-on-a-chip platform is offering researchers a powerful tool to study retinal vein occlusion, one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide. Developed by a multidisciplinary team from POSTECH in Korea, the model mimics the complex vascular and neural environment of the human retina, enabling real-time observation of disease progression and drug response. Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is often triggered by chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes. When a retinal vein becomes blocked, it leads to fluid buildup, inflammation, and abnormal blood vessel growth, ultimately resulting in irreversible vision loss. Current treatments like anti-VEGF injections and laser therapy…