“Replaceable You”: A GizmoMD Book Interview with Author Mary Roach
“We can rebuild him. We have the technology. We can make him better than he was. Better . . . stronger . . . faster.” These iconic words were part of the opening lines of the hit TV series, The Six-Million Dollar Man,…
The Latest
3D Printed Blood Vessels Expose Patient Stroke Clot Risks
Strokes often begin with tiny blood clots forming inside damaged or irregular arteries, but it has been hard to watch those first moments in action. A University of Sydney team has built small, patient‑specific models of blood vessels that let researchers see how clots start and grow under lifelike conditions. They begin with medical scans from real patients and use those as blueprints to create miniature versions of the carotid artery, the vessel in the neck that supplies blood to the brain. These printed vessels are made directly on glass, which helps blood flow more naturally through them during tests.…
Scientists Create Fully Synthetic Brain Tissue Model for Neurological Research
A new advance from the University of California, Riverside has produced the first fully synthetic brain tissue model, designed to eliminate reliance on animal-derived materials and provide a reproducible platform for studying neurological diseases. Traditional brain tissue models often depend on biological coatings such as laminin or fibrin to help cells survive, but these coatings are inconsistent and difficult to replicate. Rodent brains have also been used as stand-ins for human conditions, yet genetic and physiological differences limit accuracy. The UC Riverside innovation addresses these challenges by creating a synthetic scaffold that supports functional brain-like tissue without animal materials, aligning…
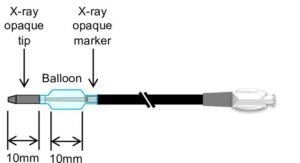
Balloon-Assisted Bronchoscopy for Safer Access to Peripheral Lung Tumors
Lung cancer remains one of the most difficult cancers to diagnose early, largely because tumors often form in the peripheral regions of the lung where conventional bronchoscopes cannot reach. While CT scans can detect small lesions, obtaining a biopsy or delivering treatment has been a major challenge. The bronchi become narrower and more complex toward the periphery, forcing clinicians to stop several centimeters short of the target. This limitation has hindered both accurate diagnosis and minimally invasive treatment options. A new technique developed at Osaka University offers a solution by using balloon-assisted bronchoscopy to safely widen the airway and create…
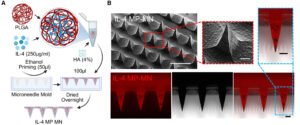
Biodegradable Microneedle Patch Heals the Heart After MI
Researchers at Texas A&M University have introduced a biodegradable microneedle patch designed to help the heart heal after a heart attack. Heart attacks deprive cardiac muscle cells of oxygen, causing them to die. The body responds by forming scar tissue, which stabilizes the heart but cannot contract like healthy muscle. This forces the remaining tissue to work harder, often leading to heart failure. The Texas A&M innovation aims to change this trajectory by delivering immune-modulating molecules directly to damaged tissue, creating a healing environment at the site of injury. The patch uses a microneedle system that penetrates the outer layer…
Amorepacific and MIT Launch Skinsight Electronic Skin Platform
South Korean beauty company Amorepacific has been recognized as a CES 2026 Innovation Award Honoree for its advanced electronic skin platform, Skinsight, developed in collaboration with researchers at MIT. This achievement highlights the company’s leadership in beauty technology and marks its seventh consecutive CES Innovation Award, underscoring a consistent track record of innovation in the intersection of science, technology, and skincare. Skinsight is designed as a next-generation wearable system that functions like electronic skin. The platform consists of three integrated components: an ultra-thin sensor patch, a compact Bluetooth transmission module, and an AI-powered mobile application. Together, these elements allow users…
Researchers Develop Injectable Antenna to Safely Power Deep Tissue Medical Implants
MIT researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking injectable antenna that could transform how medical implants are powered deep inside the human body. Traditional implants such as pacemakers or neuromodulators rely on bulky batteries or require invasive surgery for placement and maintenance. These approaches carry risks including infection, tissue damage, and repeated surgical interventions. The new antenna, developed by Associate Professor Deblina Sarkar and her group at the MIT Media Lab’s Nano-Cybernetic Biotrek, offers a safer and more efficient alternative by enabling battery-free implants that can be delivered through a simple injection. The device is a magnetoelectric antenna smaller than a grain…
Researchers Develop Magnetic Microrobots for Targeted Drug Delivery in Stroke and Cancer Treatment
A team at ETH Zurich has unveiled magnetic microrobots designed to deliver drugs directly to targeted sites in the human body, offering new possibilities for treating strokes, infections, and tumors. This innovation addresses a critical medical challenge: every year, millions of patients suffer strokes, and current therapies require high systemic doses of clot‑dissolving drugs that can cause severe side effects. By guiding medication precisely to the blocked vessel, the ETH Zurich microrobots promise safer and more effective treatment. The microrobots are engineered as spherical capsules with a soluble gel shell. Embedded within the shell are iron oxide nanoparticles that allow…
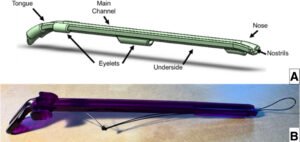
Researchers Develop New Cannula Device to Improve Hip Arthroscopy Surgery
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have introduced a breakthrough surgical device that is transforming hip arthroscopy by making procedures safer, faster, and more effective. Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery used to diagnose and treat joint problems, but traditional tools often limit precision and increase surgical time. The newly developed cannula device, formally named the CAP-LIFT cannula, provides surgeons with improved access to the hip joint, reducing complications and streamlining operations. Traditional cannulas used in hip arthroscopy often require multiple adjustments and can be difficult to position. This increases surgical time and risk, especially in complex procedures.…
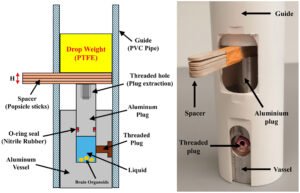
Researchers Develops Tabletop Blast Device to Study Traumatic Brain Injury
Researchers at the University of Rhode Island have introduced a tabletop blast simulator designed to investigate the long-term effects of traumatic brain injury. The innovation provides a safe and accessible way to replicate blast conditions in a laboratory setting, allowing scientists to study how explosions damage the brain over time. Unlike large-scale military testing facilities, this compact system can be deployed in standard research labs, making advanced blast injury studies more widely available. Traumatic brain injury caused by blasts is a major concern for both military personnel and civilians. While the immediate consequences of TBI are well documented, the chronic…
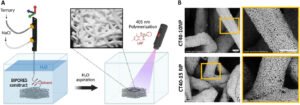
Biomaterials Reduce Medical Implant Failure by Improving Cell Integration
A Brazilian startup supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) has developed biomaterials that significantly reduce the risk of medical implant failure by improving how implants interact with human cells. The company, Extremus Smart Surfaces, is pioneering a microscopic surface treatment that transforms conventional implants into biologically active devices, accelerating healing and reducing complications. This innovation addresses a persistent problem in medicine, where implants such as dental, orthopedic, and cardiovascular devices often fail due to poor integration with surrounding tissue. Traditional implants are designed to provide mechanical support, but they do not actively engage with the biological environment. As…