Low‑Cost AI Microscope Automates Rapid Malaria Diagnosis in Low‑Resource Settings
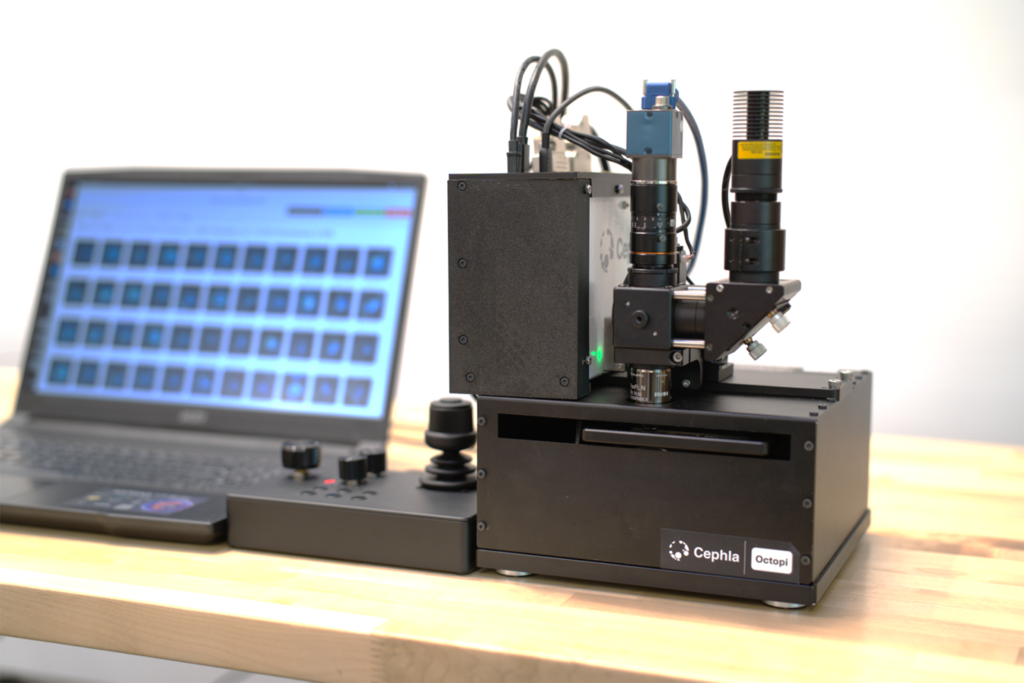
Researchers at Stanford University have developed a low cost, battery or solar powered autonomous microscope called “Octopi” that uses artificial intelligence to diagnose malaria in blood smears with far greater speed and efficiency than manual microscopy. Malaria diagnosis traditionally requires […]
Low‑Cost AI Microscope Automates Rapid Malaria Diagnosis in Low‑Resource Settings Read More »